Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 5 Lesson 16 Answer Key
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 5 Lesson 16 Problem Set Answer Key
Question 1.
Solve.
a. 3 fifths – 1 fifth = _____2 __fifths_____
Answer:
3 fifths – 1 fifth = 2 fifths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 fifths = 3/5.
3/5 = 0.6.
1 fifth = 1/5.
1/5 = 0.2.
0.6 – 0.2 = 0.4.
2/5 = 0.4.
3 fifths – 1 fifth = 2 fifths.
b. 5 fifths – 3 fifths = _____2_fifths._________
Answer:
5 fifths – 3 fifth = 2 fifths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 fifths = 5/5.
5/5 = 1.
3 fifth = 3/5.
3/5 = 0.6.
1 – 0.6 = 0.4.
2/5 = 0.4.
3 fifths – 1 fifth = 2 fifths.
c. 3 halves – 2 halves = _____1_ halves._____
Answer:
3 halves – 2 halves = 1 halves
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 halves = 3/2.
3/2 = 1.5.
2 halves = 2/2.
2/2 = 1.
1.5 – 1 = 0.5.
1/2 = 0.5.
3 halves – 2 halves = 1 half.
d. 6 fourths – 3 fourths = ____3__fourths._______
Answer:
6 fourths – 3 fourths = 3 fourths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
6 fourths = 6/4.
6/4 = 1.5.
3 fourths = 3/4.
3/4 = 0.75.
1.5 – 0.75 = 0.75.
3/4 = 0.75.
6 fourths – 3 fourths = 3 fourths.
Question 2.
Solve.
a. \(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{3}{6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 sixths = 5/6.
5/6 = 0.83.
3 sixths = 3/6.
3/6 = 0.5.
0.83 – 0.5 = 0.33.
2/6 = 0.33.
\(\frac{5}{6}\) – \(\frac{3}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
b. \(\frac{6}{8}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{8}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
6 eights = 6/8.
6/8 = 0.75.
4 eights = 4/8.
4/8 = 0.5.
0.75 – 0.5 = 0.25.
2/8 = 0.25.
\(\frac{6}{8}\) – \(\frac{4}{8}\) = \(\frac{2}{8}\)
c. \(\frac{3}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{0}{0}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 tens = 3/10.
3/10 = 0.3.
3 tens = 3/10.
3/10 = 0.3.
0.3 – 0.3 = 0.
0/6 = 0.
\(\frac{3}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{10}\) = \(\frac{0}{0}\)
d. \(\frac{5}{5}\) – \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{5}\) – \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 fifths = 5/5.
5/5 = 1.
4 fifths = 4/5.
4/5 = 0.8.
1 – 0.8 = 0.2.
1/5 = 0.2.
\(\frac{5}{5}\) – \(\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
e. \(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{4}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{4}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 fours = 5/4.
5/4 = 1.25.
4 fours = 4/4.
4/4 = 1.
1.25 – 1 = 0.25.
1/4 = 0.25.
\(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{4}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
f. \(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 fours = 5/4.
5/4 = 1.25.
3 fours = 3/4.
3/4 = 0.75.
1.25 – 0.75 = 0.5.
2/4 = 0.5.
\(\frac{5}{4}\) – \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Question 3.
Solve. Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number. Problem (a) has been completed for you.
a. 
Answer:
12/8 – 3/8 = 9/8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
12/8 – 3/8.
9/8.
9/8 = 8/8 + 1/8.
b. \(\frac{12}{6}\) – \(\frac{5}{6}\)
Answer:
12/6 – 5/6 = 7/6.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
12/6 – 5/6.
7/6.
7/6 = 6/6 + 1/6.
c. \(\frac{9}{5}\) – \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Answer:
9/5 – 3/5 = 6/5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
9/5 – 3/5.
6/5.
6/5 = 5/5 + 1/5.
d. \(\frac{14}{8}\) – \(\frac{3}{8}\)
Answer:
14/8 – 3/8 = 11/8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
14/8 – 3/8.
11/8.
11/8 = 8/8 + 3/8.
e. \(\frac{8}{4}\) – \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer:
8/4 – 2/4 = 6/4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
8/4 – 2/4.
6/4.
6/4 = 4/4 + 2/4.
f. \(\frac{15}{10}\) – \(\frac{3}{10}\)
Answer:
15/10 – 3/10 = 7/10.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
15/10 – 3/10.
7/10.
7/10 = 10/10 + 1/6.
Question 4.
Solve. Write the sum in unit form.
a. 2 fourths + 1 fourth = _3 fourths._
Answer:
2 fourths + 1 fourth = 3 fourths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
2 fourths = 1/4 + 1/4.
2 fourths + 1 fourth = 3 fourths.
1/4 + 1/4 + 1/4 = 3/4.
b. 4 fifths + 3 fifths = ____7__fifths.___
Answer:
4 fifths + 3 fifths = 7 fifths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
4 fifths = 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5.
3 fifths = 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5.
4 fifths + 3 fifths = 7 fifths.
1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 = 7/5.
Question 5.
Solve.
a. \(\frac{2}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{2}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
2 eights = 2/8.
2/8 = 0.25.
5 eights = 5/8.
5/8 = 0.625.
0.25 + 0.625 = 0.875.
7/8 = 0.875.
\(\frac{2}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\) = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
b. \(\frac{4}{12}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{4}{12}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
4 twelfths = 4/12.
4/12 = 0.33.
5 twelfths = 5/12.
5/12 = 0.41.
0.33 + 0.41 = 0.74.
9/12 = 0.74.
\(\frac{4}{12}\) + \(\frac{5}{12}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\)
Question 6.
Solve. Use a number bond to decompose the sum. Record your final answer as a mixed number.
Problem (a) has been completed for you.
a. 
Answer:
3/5 + 4/5 = 7/5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
3/5 + 4/5.
7/5.
7/5 = 5/5 + 2/5.
b. \(\frac{4}{4}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
4/4 + 3/4 = 7/4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
4/4 + 3/4.
7/4.
7/4 = 4/4 + 3/4.
c. \(\frac{6}{9}\) + \(\frac{6}{9}\)
Answer:
6/9 + 6/9 = 12/9.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
6/9 + 6/9.
12/9.
12/9 = 9/9 + 3/9.
d. \(\frac{7}{10}\) + \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Answer:
7/10 + 6/10 = 13/10.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
7/10 + 6/10.
13/10.
13/10 = 10/10 + 3/10.
e. \(\frac{5}{6}\) + \(\frac{7}{6}\)
Answer:
5/6 + 7/6 = 12/6.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
5/6 + 7/6.
12/6.
12/6 = 6/6 + 7/6.
f. \(\frac{9}{8}\) + \(\frac{5}{8}\)
Answer:
9/8 + 5/8 = 14/8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
9/8 + 5/8.
14/8.
14/8 = 8/8 + 6/8.
Question 7.
Solve. Use a number line to model your answer.
a. \(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
7 fours = 7/4.
7/4 = 1.75.
5 fours = 5/4.
5/4 = 1.25.
1.75 – 1.25 = 0.5.
2/4 = 0.5.
\(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\)
b. \(\frac{5}{4}\) + \(\frac{2}{4}\)
Answer:
5/4 + 2/4 = 7/4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
5/4 + 2/4.
7/4.
7/4 = 4/4 + 3/4.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 5 Lesson 16 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Question 1.
Solve. Use a number bond to decompose the difference. Record your final answer as a mixed number.
\(\frac{16}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{9}\)
Answer:
16/9 – 5/9 = 11/9.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
16/9 – 5/9.
11/9.
11/9 = 9/9 + 2/9.
Question 2.
Solve. Use a number bond to decompose the sum. Record your final answer as a mixed number.
\(\frac{5}{12}\) + \(\frac{10}{12}\)
Answer:
5/12 + 10/12 = 15/12.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
5/12 + 10/12.
15/12.
15/12 = 12/12 + 3/12.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 5 Lesson 16 Homework Answer Key
Question 1.
Solve.
a. 3 sixths – 2 sixths = __1__sixths___________
Answer:
3 sixths – 2 sixths = 1 sixths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 sixths = 3/6.
3/6 = 0.5.
2 sixths = 2/6.
2/6 = 0.33.
0.5 – 0.3 = 0.1.
1/6 = 0.1.
b. 5 tenths – 3 tenths = ___2 tenths._____
Answer:
5 tenths – 3 tenths = 2 tenths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 tenths = 5/10.
5/10 = 0.5.
3 tenths = 3/10.
3/10 = 0.3.
0.5 – 0.3 = 0.2.
2/10 = 0.2.
c. 3 fourths – 2 fourths = ____1__fourth._________
Answer:
3 fourths – 2 fourths = 1 fourth.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 fourths = 3/4.
3/4 = 0.75.
2 fourths = 2/4.
2/4 = 0.5.
0.75 – 0.5 = 0.25.
1/4 = 0.25.
d. 5 thirds – 2 thirds = ___3__thirds._____
Answer:
5 thirds – 2 thirds = 3 thirds.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 thirds = 5/3.
3/5 = 1.6.
2 thirds = 2/3.
2/3 = 0.6.
1.6 – 0.6 = 1.
3/3 = 1.
Question 2.
Solve.
a. \(\frac{3}{5}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{3}{5}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
3 fives = 3/5.
3/5 = 0.6.
2 fives = 2/5.
2/5 = 0.4.
0.6 – 0.4 = 0.2.
1/5 = 0.2.
\(\frac{3}{5}\) – \(\frac{2}{5}\) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
b. \(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{9}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{4}{9}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
7 nines = 7/9.
7/9 = 0.7.
3 nines = 3/9.
3/9 = 0.3.
0.7 – 0.3 = 0.4.
4/9 = 0.4.
\(\frac{7}{9}\) – \(\frac{3}{9}\) = \(\frac{4}{9}\)
c. \(\frac{7}{12}\) – \(\frac{3}{12}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{12}\) – \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
7 twelfths = 7/12.
7/12 = 0.58.
3 twelfths = 3/12.
3/12 = 0.25.
0.58 – 0.25 = 0.33.
4/12 = 0.33.
\(\frac{7}{12}\) – \(\frac{3}{12}\) = \(\frac{4}{12}\)
d. \(\frac{6}{6}\) – \(\frac{4}{6}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{6}{6}\) – \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
6 sixs = 6/6.
6/6 = 1.
4 sixs = 4/6.
4/6 = 0.6.
1 – 0.6 = 0.4.
2/6 = 0.4.
\(\frac{6}{6}\) – \(\frac{4}{6}\) = \(\frac{2}{6}\)
e. \(\frac{5}{3}\) – \(\frac{2}{3}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{5}{3}\) – \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{3}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
5 threes = 5/3.
5/3 = 1.6.
2 threes = 2/3.
2/3 = 0.6.
1.25 – 1 = 0.25.
3/3 = 1.
\(\frac{5}{3}\) – \(\frac{2}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{3}\)
f. \(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
7 fours = 7/4.
7/4 = 1.75.
5 fours = 4/4.
5/4 = 1.25.
1.75 – 1.25 = 0.75.
3/4 = 0.75.
\(\frac{7}{4}\) – \(\frac{5}{4}\) = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 3.
Solve. Use a number bond to decompose the difference. Record your final answer as a mixed number. Problem (a) has been completed for you.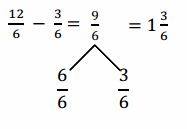
Answer:
12/6 – 3/6 = 9/6.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
12/6 – 3/4.
9/6.
9/6 = 6/6 + 3/6.
b. \(\frac{17}{8}\) – \(\frac{6}{8}\)
Answer:
17/8 – 6/8 = 11/8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
17/8 – 6/8.
11/8.
11/8 = 8/8 + 2/8.
c. \(\frac{9}{5}\) – \(\frac{3}{5}\)
Answer:
9/5 – 3/5 = 6/5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
9/5 – 3/5.
6/5.
6/5 = 5/5 + 1/6.
d. \(\frac{11}{4}\) – \(\frac{6}{4}\)
Answer:
11/4 – 6/4 = 5/4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
11/4 – 6/4.
5/4.
5/4 = 4/4 + 1/4.
e. \(\frac{10}{7}\) – \(\frac{2}{7}\)
Answer:
10/7 – 2/7 = 8/7.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
10/7 – 2/7.
8/7.
8/7 = 7/7 + 1/7.
f. \(\frac{21}{10}\) – \(\frac{9}{10}\)
Answer:
21/10 – 9/10 = 11/10.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
21/10 – 9/10.
11/10.
11/10 = 10/10 + 1/10.
Question 4.
Solve. Write the sum in unit form.
a. 4 fifths + 2 fifths = ____6__fifths.____
Answer:
4 fifths + 2 fifths = 6 fifths.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
4 fifths = 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5.
2 fifths = 1/5 + 1/5.
4 fifths + 2 fifth = 6 fifths.
1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 + 1/5 = 6/5.
b. 5 eighths + 2 eighths = __7___eights.______
Answer:
5 eights + 2 eighths = 7 eights.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to show how to convert the difference to a mixed number.
5 eights = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8.
2 eights = 1/8 + 1/8.
5 eights + 2 eights = 7 eights.
1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8 = 7/8.
Question 5.
Solve.
a. \(\frac{3}{11}\) + \(\frac{6}{11}\)
Answer:
3/11 + 6/11 = 9/11.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
3/11 + 6/11.
9/11.
9/11 = 3/11 + 9/11.
b. \(\frac{3}{10}\) + \(\frac{6}{10}\)
Answer:
3/10 + 6/10 = 9/10.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
3/10 + 6/10.
9/10.
9/10 = 3/10 + 6/10.
Question 6.
Solve. Use a number bond to decompose the sum. Record your final answer as a mixed number.
a. \(\frac{3}{4}\) + \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Answer:
3/4 + 3/4 = 6/4.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
3/4 + 3/4.
6/4.
6/4 = 4/4 + 5/4.
b. \(\frac{8}{12}\) + \(\frac{6}{12}\)
Answer:
8/12 + 6/12 = 14/12.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
8/12 + 6/12.
14/12.
14/12 = 12/12 + 2/12.
c. \(\frac{5}{8}\) + \(\frac{7}{8}\)
Answer:
5/8 + 7/8 = 12/8.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
5/8 + 7/8.
12/8.
12/8 = 8/8 + 4/8.
d. \(\frac{8}{10}\) + \(\frac{5}{10}\)
Answer:
8/10 + 5/10 = 13/10.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
8/10 + 5/10.
13/10.
13/10 = 10/10 + 3/10.
e. \(\frac{3}{5}\) + \(\frac{6}{5}\)
Answer:
3/5 + 6/5 = 9/5.
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
Use a number bond to decompose the sum.
3/5 + 6/5.
9/5.
9/5 = 5/5 + 4/5.
Question 7.
Solve. Use a number line to model your answer.
a. \(\frac{11}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{9}\)
Answer:
\(\frac{11}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{9}\) = \(\frac{6}{9}\)
Explanation:
In the above-given question,
given that,
11 nines = 11/9.
11/9 = 0.58.
5 nines = 5/9.
5/9 = 0.25.
0.58 – 0.25 = 0.33.
6/9 = 0.33.
\(\frac{11}{9}\) – \(\frac{5}{9}\) = \(\frac{6}{1}\)
b. \(\frac{13}{12}\) + \(\frac{4}{12}\)